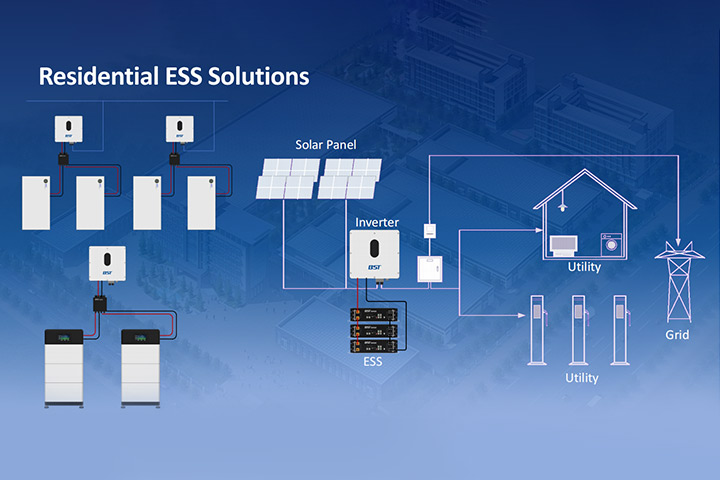
Part I: What is a 26650 Battery?

The 26650 battery is a lithium-ion rechargeable battery with a standardized cylindrical size of 26mm in diameter and 65mm in length. These batteries are known for their high capacity, durability, and stable output, making them a popular choice in a variety of applications, including:
- Flashlights: Providing long-lasting, high-lumen performance.
- Power Tools: Delivering consistent power for heavy-duty applications.
- Energy Storage Systems: These are used in home and portable energy storage devices.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Supporting auxiliary and backup power needs.
- Medical Devices: Reliable energy source for critical equipment.
Their versatility and robust design make them suitable for both consumer and industrial applications.
Part II: What to Pay Attention to When Using 26650 Batteries
While 26650 batteries offer excellent performance, safe usage, and maintenance practices are essential to maximize their lifespan and prevent potential hazards. Below are detailed guidelines:
1. Battery Specification and Compatibility
- Verify whether your device supports the 26650 battery size to prevent size mismatches.
- Ensure the battery’s rated voltage, capacity, and discharge current meet the device’s requirements.
2. Charger Selection
- Use a dedicated lithium-ion charger designed for 26650 batteries.
- Maintain a charging voltage of 4.2V and select a charging current that does not exceed 0.5C-1C of the battery’s capacity. For instance, a 5000mAh battery should charge at a maximum of 2.5A to 5A.
3. Battery Protection Circuit
- Opt for batteries with built-in protection circuits to safeguard against overcharging, over-discharging, and short circuits.
- If using unprotected batteries, pair them with a compatible protection circuit board for enhanced safety.
4. Temperature Management
- Operate within the typical temperature range of -20°C to 60°C.
- Avoid extreme heat, which may cause thermal runaway, and extreme cold, which can degrade performance.
5. Avoid Overcharging and Over discharging

- Do not leave the battery in the charger for extended periods.
- Recharge promptly if the voltage drops below 2.5V to prevent irreversible capacity loss.
6. Proper Storage
- Store unused batteries at around 50% charge in a cool, dry environment.
- Avoid contact with metal objects to prevent accidental short circuits.
7. Prevent Physical Damage
- Handle batteries carefully to avoid crushing, puncturing, or dropping them.
- Discontinue use if the casing is deformed or damaged.
8. Safe Operation
- Avoid mixing old and new batteries or using batteries of different brands.
- Always install batteries with the correct polarity.
9. Disposal of Used Batteries
- Dispose of used batteries through certified recycling programs.
- Never discard batteries in regular trash to avoid environmental harm.
By following these precautions, you can ensure the safety, longevity, and optimal performance of 26650 batteries.
Part III: Methods of Testing the Health of 26650 Batteries
Testing a 26650 battery’s health involves a series of evaluations to determine its performance, safety, and reliability. Each test includes the purpose, method, and passing standard.
1. Charge and Discharge Test
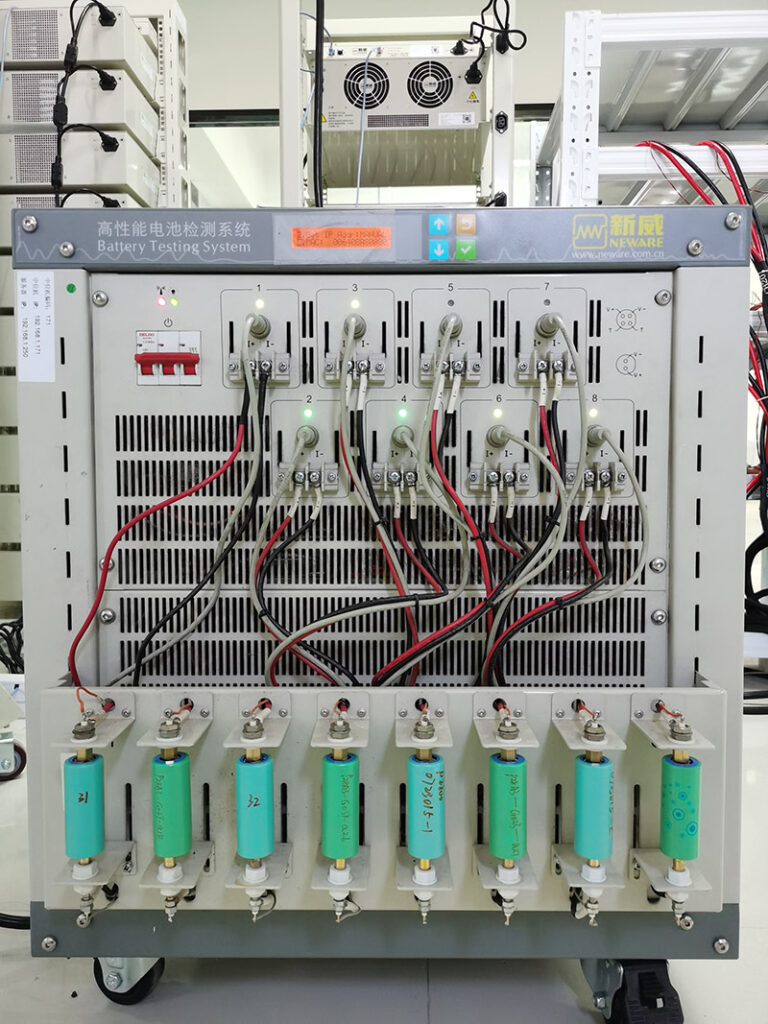
- Purpose: Assess battery capacity and efficiency.
- Method: Fully charge the battery and discharge it under a constant load. Record the capacity (mAh).
- Passing Standard: Capacity should be at least 80% of the rated value.
2. Multiplier Test
- Purpose: Measure performance under various loads.
- Method: Discharge the battery at different currents (e.g., 0.5C, 1C, 2C).
- Passing Standard: Voltage drop and heat generation should remain within safe limits.
3. Storage Test (Ambient Temperature)

- Purpose: Evaluate self-discharge rate.
- Method: Charge the battery, store it at room temperature for one month, and recheck capacity.
- Passing Standard: Capacity loss should not exceed 5%.
4. Hot and Cold Cycle
- Purpose: Test resilience to temperature changes.
- Method: Cycle the battery between -20°C and 60°C for 20 cycles.
- Passing Standard: No visible damage; capacity loss <10%.
5. High and Low-Temperature Test
- Purpose: Assess performance extremes.
- Method: Test capacity at -20°C and 60°C.
- Passing Standard: Capacity should remain above 70% of the rated value.
6. Capacity Test

- Purpose: Determine the battery’s actual capacity.
- Method: Fully discharge and recharge the battery; measure capacity.
- Passing Standard: Within 90% of the rated capacity.
7. Short Circuit Test
- Purpose: Test safety against short circuits.
- Method: Short the battery terminals briefly under controlled conditions.
- Passing Standard: No fire or explosion; protective mechanisms should engage.
8. Rate Test
- Purpose: Assess discharge capability.
- Method: Discharge at high rates (e.g., 3C-5C).
- Passing Standard: Minimal voltage drop; no overheating.
9. Free Fall Test
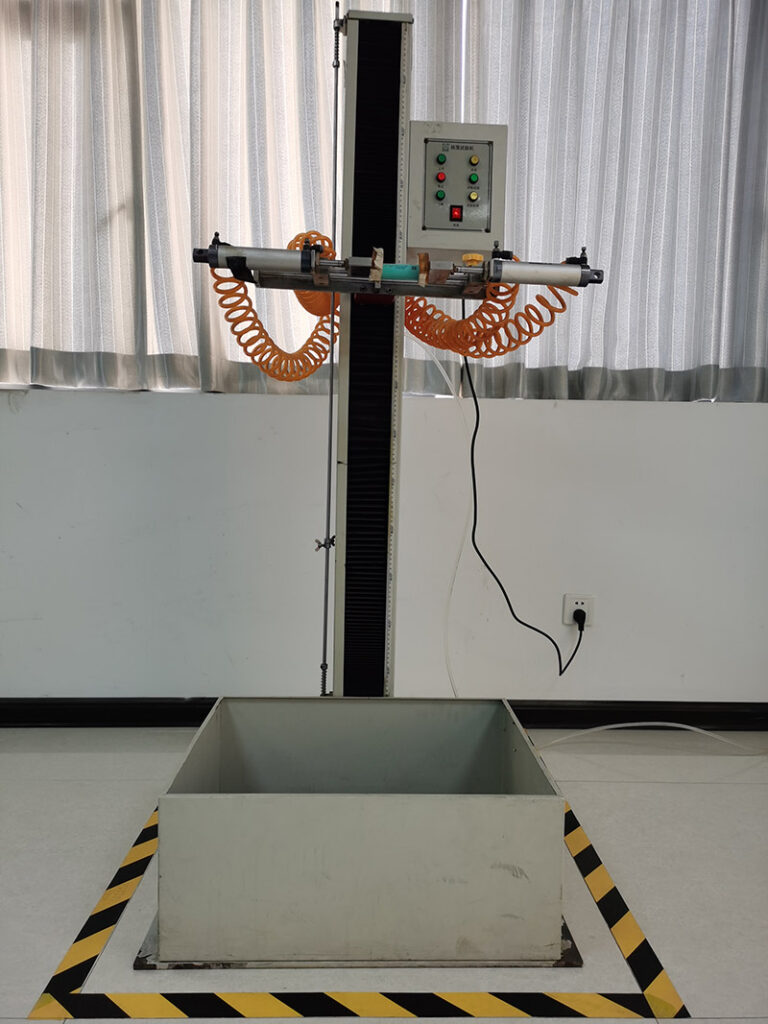
- Purpose: Test physical durability.
- Method: Drop the battery from 1m height onto a hard surface.
- Passing Standard: No leakage, deformation, or performance loss.
10. Vibration Test
- Purpose: Simulate transportation stresses.
- Method: Vibrate the battery at varying frequencies.
- Passing Standard: No physical damage or capacity loss.
11. Nail Penetration Test
- Purpose: Evaluate internal short circuit safety.
- Method: Drive a nail through the battery.
- Passing Standard: No fire or explosion.
12. Impact Test
- Purpose: Assess safety against impacts.
- Method: Apply a weight drop onto the battery.
- Passing Standard: No fire or leakage.
13. Shattering Test
- Purpose: Test resistance to external pressure.
- Method: Apply crushing force.
- Passing Standard: No leakage or ignition.
14. Flame Test
- Purpose: Assess flammability resistance.
- Method: Expose the battery to an open flame for a specified duration.
- Passing Standard: No explosion or sustained combustion.
Part IV: Importance of Testing the Health of 26650 Batteries

- Safety Assurance: Prevent accidents caused by thermal runaway, short circuits, or overcharging.
- Performance Optimization: Ensure the battery delivers optimal energy for its intended application.
- Extended Lifespan: Identify and mitigate issues early to prolong battery life.
- Regulatory Compliance: Meet safety standards and certifications.
- Cost Efficiency: Avoid premature replacement and reduce maintenance costs.
Part V: Summary

The 26650 battery is a versatile and powerful energy source. Ensuring its health through proper usage, regular testing, and maintenance is crucial for safety, performance, and longevity. By following best practices and conducting detailed health tests, users can maximize their investment and contribute to sustainable energy solutions.
Part VI: 10 FAQs About 26650 Batteries
- What is a 26650 battery?
A cylindrical lithium-ion battery with a diameter of 26 mm and length of 65 mm. - How do I charge a 26650 battery?
Use a lithium-ion charger, maintaining a voltage of 4.2V and a current of 0.5C-1C. - What are the common uses of 26650 batteries?
Flashlights, power tools, and energy storage systems. - Can I mix 26650 batteries with other sizes?
No, always use batteries of the same size and type. - How do I test the capacity of a 26650 battery?
Fully charge and discharge the battery, recording its energy output. - What should I do if my 26650 battery overheats?
Stop using it immediately and inspect for damage. - How do I store a 26650 battery long-term?
Charge to 50% and store away from metal objects in a cool, dry place. - Are 26650 batteries safe?
Yes, if used correctly and with built-in protection circuits. - What is the typical lifespan of a 26650 battery?
Around 300-500 charge cycles with proper use. - How do I dispose of a 26650 battery?
Take it to a professional recycling center to prevent environmental harm.
By understanding these aspects, users can safely and effectively use 26650 batteries while maintaining optimal performance.