The shift to renewable energy has sparked a profound transformation in the global energy market, where energy storage systems (ESS) are playing an increasingly central role. With over 22 years of experience in the energy storage industry, BST is at the forefront of this change. In this article, we explore what an energy storage system is, how it works, the benefits it offers, and why its importance will only continue to grow. As renewable energy becomes more prevalent, ESS supports the grid, stabilizes energy supply, and optimizes energy use—essential for a low-carbon, resilient energy future.
What is an Energy Storage System?
An energy storage system (ESS) is a solution that captures and stores energy for later use, improving the reliability and efficiency of the power supply. ESS can be powered by various sources, including renewables like solar or wind, and it can store electricity from the grid during off-peak hours. By ensuring that energy is available when needed, ESS aligns power supply with demand, bolsters grid stability, and reduces energy costs.

With ESS, consumers can tap into stored energy when needed, allowing for greater independence from the grid. Energy storage is also available at various scales, from residential systems supporting homes to large-scale installations powering cities. Through this adaptability, ESS plays a crucial role across the entire energy landscape.
—
How Does an Energy Storage System Work?
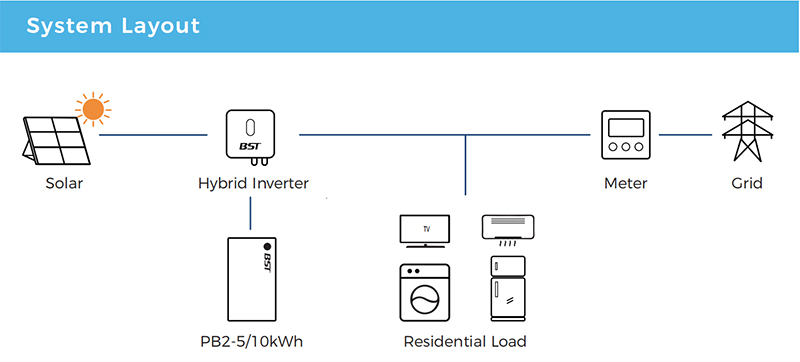
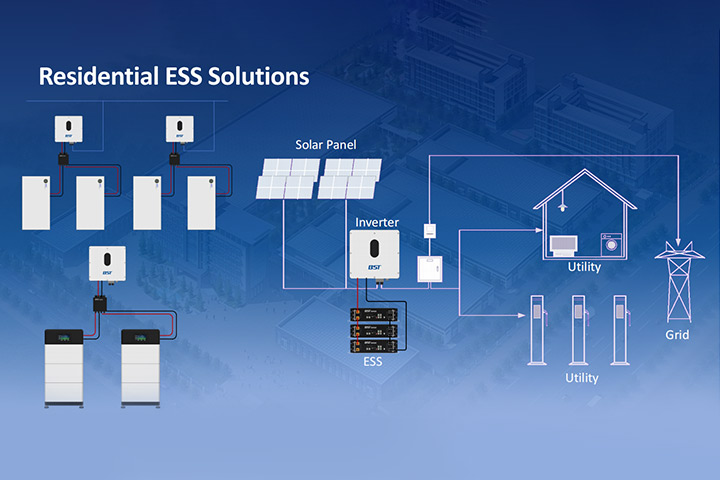
The operation of energy storage systems involves three core stages:
1>. Energy Capture: ESS collects energy from renewable sources, such as solar panels, or directly from the grid. By capturing energy when supply exceeds demand or when grid prices are low, ESS maximizes resource utilization.
2>. Energy Storage: The energy is then stored in batteries—typically lithium-ion due to their high energy density and efficiency—or other forms such as pumped hydro or thermal storage. These systems store excess power during low-demand periods.
3>. Energy Discharge: When energy demand rises, or during peak pricing periods, the ESS releases stored energy. This flexibility ensures users can access cost-effective energy even when prices are high or supply is limited, optimizing the flow and balance of power.
This cycle enables ESS to align power supply with demand, provide backup power, and stabilize the grid, playing a critical role in the modern energy system.
—
What Are the Advantages of Energy Storage Systems?
The advantages of energy storage systems extend beyond cost savings and grid resilience. ESS enhances energy security, promotes environmental sustainability, and reduces costs across the energy market. Key benefits include:
Enhanced Reliability and Resilience: ESS ensures a steady power supply, providing a backup source during outages or emergencies, which is especially critical in locations with unreliable grid infrastructure.
Reduced Energy Costs: By allowing users to store energy during off-peak times and use it during peak demand, ESS offers significant cost savings, which is beneficial for both residential and commercial users.
Greater Environmental Sustainability: ESS makes renewables like solar and wind more dependable by smoothing out their inherent variability. This aligns with global climate goals, supporting a shift toward a cleaner energy mix.
Improved Efficiency: ESS captures energy that would otherwise go unused and discharges it when demand spikes, reducing waste and enhancing system efficiency.
Grid Stabilization: Energy storage systems can quickly respond to grid fluctuations, offering frequency regulation and helping prevent blackouts.
Energy storage systems are indispensable to a sustainable energy future, providing stability, reliability, and efficiency.
—
What Are the Application Scenarios for Residential Energy Storage Systems?
Energy storage systems serve different roles depending on their point of integration in the energy network. Broadly, these applications are divided into three main areas: the generation side, the grid side, and the user side.
Generation Side
On the generation side, energy storage balances the supply and demand of intermittent renewable resources, such as solar and wind. By storing excess power, ESS ensures that energy is available even when production fluctuates. For instance, solar energy captured during the day can be stored for use at night, enabling renewable resources to contribute consistently.
Grid Side
On the grid side, ESS serves as a load-balancing tool. During off-peak hours, ESS absorbs surplus electricity and discharges it during peak hours. This demand management reduces the need for costly infrastructure upgrades and minimizes the risk of blackouts, enabling a more resilient and efficient grid.
User Side
On the user side, residential energy storage systems empower homeowners to store energy generated from rooftop solar panels. This energy can be used during the evening, saving costs and enhancing energy independence. For businesses, ESS offers reliable power backup, shielding them from disruptions and protecting critical operations.
Together, these applications demonstrate the versatility of ESS, which enhances energy security, supports grid reliability and enables renewable integration across the board.
—
Why Use Energy Storage Systems?
The demand for energy storage technology has grown sharply in response to several critical needs in the modern energy landscape:
1>. Balancing Energy Supply
Renewables are essential to a sustainable energy future but are naturally intermittent. ESS balances these fluctuations by storing energy when production is high and discharging it when demand rises, stabilizing the supply-demand curve.
2>. Improved Energy Utilization
Without storage, surplus energy often goes to waste. ESS captures this surplus, allowing it to be used when needed, improving overall energy utilization and reducing waste.
3>. Regulating the Grid Load
By discharging energy during peak demand and storing it during off-peak hours, ESS helps flatten demand spikes and smooth out troughs. This load management prevents strain on the grid, reducing the need for costly peak-time generation.
4>. Enhancing Grid Stability
ESS provides rapid-response support to the grid by maintaining frequency stability, offering ancillary services that reduce the likelihood of blackouts, and help stabilize renewable-heavy grids.
5>. Emergency Backup Power
Energy storage systems provide essential backup during outages, ensuring the reliability of power for hospitals, data centers, and households. This emergency power capability also enhances resilience against extreme weather events and unforeseen disruptions.
6>. Addressing the Energy Crisis
With fossil fuel reserves declining, ESS is essential for integrating renewables, which mitigates the need for traditional, polluting sources. This shift reduces carbon emissions, promoting a sustainable and secure energy future.
These factors underscore why energy storage technology is becoming indispensable in the transition to a reliable and sustainable energy grid.
—
How Does Energy Storage Bring Economic Benefits?
The economic advantages of ESS are considerable, impacting both individual users and the broader energy infrastructure. Key economic benefits include:
Lower Electricity Bills: ESS enables consumers to buy electricity during low-rate periods, store it, and use it during peak-rate times. These cost savings add up significantly for both households and businesses.
Deferred Infrastructure Costs: For utilities, ESS reduces the need for expensive infrastructure upgrades, like new power plants or substations, by balancing load demands on the existing grid.
Enhanced ROI on Renewables: ESS increases the value of renewable energy by making it available on demand, thereby maximizing the return on investment for both solar and wind systems.
New Revenue Streams: Through services like frequency regulation and demand response, energy storage systems open new revenue streams for both commercial users and utility companies.
The economic potential of ESS goes beyond energy savings to encompass infrastructure savings, greater renewable returns, and increased resilience against market volatility.
—
Where is the Future of the Energy Storage Market?
The energy storage market is on an upward trajectory. With growing demand for renewable energy integration, ESS is becoming central to the new energy economy. Several factors are shaping the future of this market:
1>. Government Policies and Incentives: Many countries are actively supporting ESS with grants, tax breaks, and incentives to encourage adoption. This backing will likely continue to accelerate market growth.
2>. Technological Innovations: Emerging technologies, like solid-state batteries, offer greater safety, efficiency, and longer life spans. These innovations will reduce costs and make ESS more accessible and sustainable.
3>. Economies of Scale: As the market expands, costs are expected to decrease, making ESS viable for a broader range of users and applications. Battery costs have fallen by over 85% in the last decade and are projected to continue decreasing.
4>. Energy Independence Demand: Consumers and businesses are seeking energy security and independence from the grid. ESS is an ideal solution for achieving this self-reliance, especially in regions with high electricity prices or unreliable grid access.
5>. Global Sustainability Goals: With global carbon reduction targets, energy storage is crucial in supporting renewables and decreasing dependence on fossil fuels.
The ESS market is forecasted to experience a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% from 2025 to 2030, driven by these factors.
—
Conclusion: Summing Up Key Insights on Energy Storage Systems
In reviewing the key questions surrounding energy storage systems, several trends and opportunities become evident. ESS is transforming the energy market by ensuring a stable, efficient, and cost-effective power supply. By balancing energy supply and demand, enhancing grid stability, and providing backup power, ESS addresses modern energy challenges and supports the rise of renewables. The technology offers undeniable economic and environmental benefits, creating a robust foundation for a low-carbon energy future.
BST, with over two decades of expertise, offers a diverse range of energy storage products tailored to residential and commercial applications. From wall-mounted residential systems to industrial-scale solutions, BST’s energy storage products deliver reliability, cost savings, and sustainability. As the global market grows, BST continues to innovate, making energy storage accessible and practical for all. The future of energy storage is not only promising but necessary, and with pioneers like BST, it is quickly becoming a reality for a sustainable world.