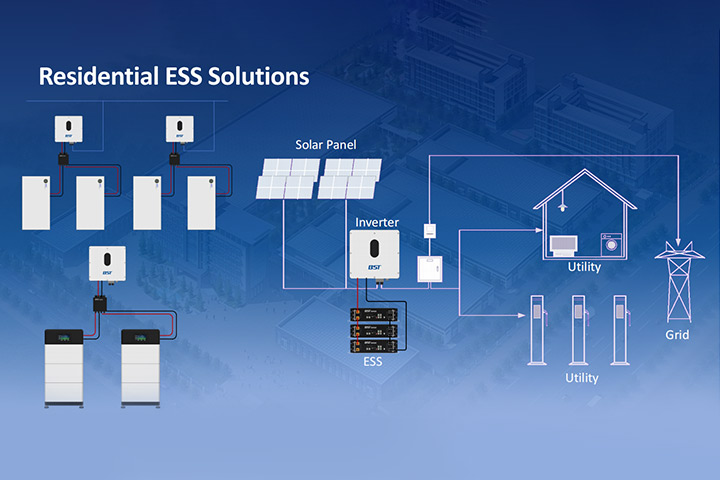
Home energy storage systems are becoming increasingly popular as renewable energy adoption grows. These systems typically include a battery bank, a charger, and an inverter, allowing homeowners to store surplus electricity generated by solar panels or other renewable energy sources for later use. The benefits range from energy independence to cost savings, but there are also challenges to consider. Below, we provide a comprehensive analysis of the advantages and disadvantages of home energy storage systems, enhanced with detailed insights.

Current Market Overview
The global home energy storage market is expanding rapidly. According to a 2023 report, the market size was valued at approximately $6 billion, with projections indicating a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 20% through 2030. The adoption is driven by factors like declining battery costs, rising electricity prices, and government incentives promoting renewable energy use. Europe leads in adoption, driven by stringent carbon emission targets, followed by North America and Asia-Pacific.
With advancements in technology and increased environmental awareness, home energy storage systems are seen as a cornerstone of sustainable living. Yet, understanding their pros and cons is critical for consumers considering an investment.
Advantages of Home Energy Storage Systems
1. Energy Saving and Emission Reduction
Home energy storage systems allow homeowners to store excess energy from renewable sources like solar panels. This stored energy reduces reliance on the grid, lowering the demand for electricity generated from fossil fuels. By reducing traditional energy consumption, these systems significantly contribute to lower greenhouse gas emissions.
For example, a study showed that households using solar-plus-storage systems cut their carbon footprints by up to 30%. These systems align with global goals for reducing carbon emissions and promoting green energy.
2. Enhanced Energy Independence
A home energy storage system empowers households to become less dependent on the utility grid. It enables users to store the energy they generate and use it when needed, such as during blackouts or peak demand periods. This autonomy ensures that homeowners have access to electricity even in remote locations or areas with unstable grids.
In regions prone to power outages, energy storage systems provide reliable backup, enhancing convenience and peace of mind.
3. Reduced Electricity Costs
Energy storage systems enable homeowners to optimize electricity usage by leveraging time-of-use pricing. They can store energy during off-peak hours when electricity is cheaper and use it during peak times when rates are higher.
In areas with high electricity tariffs, this strategy can lead to significant savings. For instance, some users have reported up to 40% reductions in annual electricity bills by pairing energy storage with solar power.
4. Emergency Backup Power
Energy storage systems act as a reliable power backup during emergencies, such as natural disasters or grid failures. They ensure that essential appliances, like refrigerators and medical devices, keep running.
Unlike traditional generators, which rely on fuel, battery backups are silent, environmentally friendly, and automatically activated during outages. This seamless operation makes them a safer and more efficient alternative.
5. Integration with Smart Technology
Modern energy storage systems are designed to integrate with smart home technologies, allowing users to monitor and control their energy usage in real-time. Mobile apps and dashboards provide insights into energy production, storage levels, and consumption patterns.
This level of control helps homeowners make informed decisions, such as reducing waste or scheduling appliance usage during optimal times.
Disadvantages of Home Energy Storage Systems
1. High Initial Costs
The upfront cost of installing a home energy storage system remains a significant barrier for many households. Depending on the system size and battery type, expenses can range from $5,000 to $20,000 or more. While government incentives and tax credits help offset these costs, the payback period can be lengthy, especially in areas with lower electricity rates.
2. Limited Battery Lifespan
Home energy storage systems rely on batteries, which degrade over time. Lithium-ion batteries, the most commonly used type, typically last 10–15 years or about 5,000 charge cycles. After this period, replacement is necessary, which adds to long-term costs.
Battery performance also diminishes in extreme temperatures, requiring additional climate control measures in some cases.
3. Complex Installation Process
Installing a home energy storage system requires professional expertise. It involves integrating various components, such as the inverter, batteries, and existing electrical system. Improper installation can lead to safety hazards, including electrical fires or system malfunctions.
Finding qualified installers can be challenging in some regions, further complicating the adoption process.
4. Limited Storage Capacity
Home energy storage systems have finite storage capacities, which may not suffice for households with high energy demands. For example, a 10 kWh battery might only power essential appliances for a few hours during a blackout.
Scaling up capacity requires additional batteries, which increases costs and space requirements. This limitation underscores the importance of proper system sizing based on individual needs.
5. Environmental Concerns Related to Batteries
While energy storage systems promote green energy, the environmental impact of battery production and disposal is a concern. Mining for materials like lithium and cobalt involves significant ecological and ethical issues. Additionally, improper disposal of batteries can lead to soil and water contamination.
Efforts are underway to develop sustainable battery technologies and recycling programs, but these challenges persist.
Future Development and Trends

The future of home energy storage systems is promising, with several trends shaping the market:
- Declining Battery Costs: Technological advancements and economies of scale are driving down battery prices, making systems more accessible to average consumers.
- Increased Efficiency: Innovations like solid-state batteries promise higher energy densities and longer lifespans.
- Government Policies: Supportive policies, such as tax incentives and renewable energy mandates, will accelerate adoption.
- Grid Integration: Future systems will play a vital role in decentralized energy grids, where homes not only consume but also supply energy to the grid.
- Focus on Sustainability: Companies are investing in eco-friendly battery materials and recycling programs to address environmental concerns.
Conclusion
Home energy storage systems offer numerous advantages, including energy savings, independence, and emergency backup power. However, challenges such as high costs, limited lifespans, and installation complexities need to be addressed. As technology evolves and costs decline, these systems are poised to become integral to sustainable living.
By adopting home energy storage, households can reduce their carbon footprints, save on electricity costs, and gain energy independence. While challenges remain, the long-term benefits make these systems a worthwhile investment for a greener future.