In an era where sustainable energy solutions are increasingly sought after, understanding the role of energy storage has become essential. A Residential Energy Storage System (RESS) serves as a pivotal technology in this landscape, enabling homeowners to store excess electricity generated, particularly from renewable sources like solar panels. By seamlessly integrating storage and consumption, RESS helps balance energy supply and demand, ensuring efficient use of renewable energy and providing a reliable power source during outages. This introduction sets the stage for a deeper exploration of the concept and benefits of RESS, highlighting its significance in modern energy management.
Concept of Energy Storage System
Traditionally, the electrical grid operates on the principle that the electricity produced must be consumed immediately. This means that at any given moment, the amount of electricity generated must match the amount used by consumers. In grid-connected photovoltaic (PV) systems, excess electricity that is not consumed by the load is absorbed by the grid. This balance is essential to maintain the stability and reliability of the power supply.
However, modern industrial advancements have introduced the concept of energy storage, allowing for the temporary storage of electricity by converting it into other forms of energy and then reconverting it back into electricity when needed. This capability enables the transfer of energy across different time scales and geographical locations, providing flexibility in energy management and usage. Energy storage technologies include batteries, thermal storage, flywheels, and more, each with unique characteristics and applications. The technology that enables this is known as energy storage technology.
Energy storage systems (ESS) are defined as systems that store energy by converting electrical energy into other forms and then back into electrical energy when required. This process allows for better management of energy supply and demand, enabling users to store energy during off-peak periods or when renewable energy production is high and use it during peak periods or when renewable energy production is low. This not only helps balance the grid but also promotes the use of renewable energy sources.

Household Energy Storage System
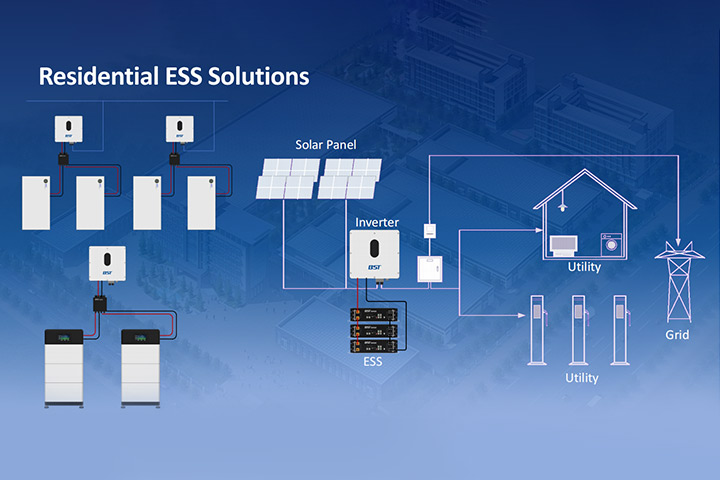
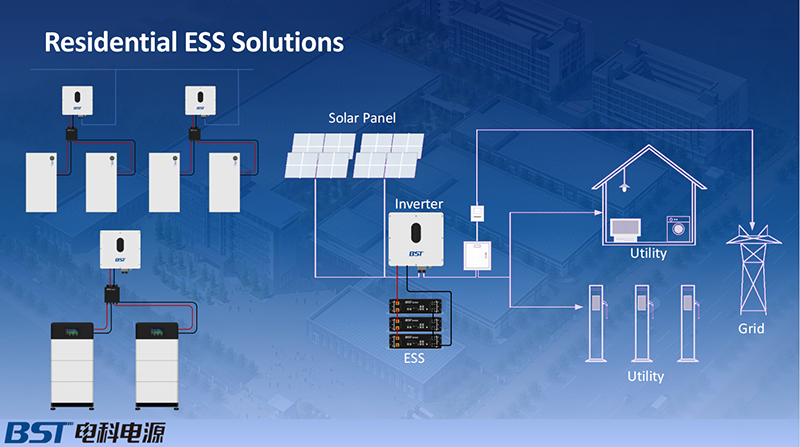
A Residential Energy Storage System (RESS) is a specific application of ESS, tailored for use in residential settings. RESS is increasingly becoming popular in regions like North America, Europe, and Oceania, where it has reached a market scale. Typically integrated with solar power generation systems, RESS allows homeowners to store excess energy generated by their solar panels and use it when needed, thereby reducing reliance on the grid.
RESS primarily consists of two core components: the battery and the inverter. The battery serves as the storage medium for electricity. To ensure efficiency and safety, it must meet criteria such as high safety standards, long lifespan, and high energy density. These characteristics are crucial as they directly affect the performance and longevity of the storage system. The inverter, on the other hand, functions as the power output interface, converting the stored DC power into AC power that can be used by household appliances. High reliability, intelligence, and efficiency are essential qualities for inverters, as they ensure seamless operation and integration with other energy systems.
The integration of RESS with residential PV systems offers several benefits. It enables homeowners to maximize their self-consumption of solar energy, using the stored energy during periods of low solar generation or high demand. This capability significantly reduces electricity bills, potentially cutting them by up to 80% annually. Additionally, RESS provides a backup power supply during grid outages, enhancing the resilience and energy security of households.
The Role and Convenience of Residential Energy Storage Systems
The role of RESS extends beyond mere energy storage; it offers substantial convenience and benefits to homeowners. One of the primary advantages is the financial savings achieved by reducing electricity purchases from the grid. By storing excess solar energy, homeowners can use this stored energy during peak times when electricity prices are higher, thus avoiding costly grid electricity. This not only reduces energy costs but also offers a return on investment for those who have installed solar PV systems.
Moreover, RESS contributes to environmental sustainability by facilitating the increased use of renewable energy sources. By storing and utilizing solar energy, households can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and reliance on fossil fuels. This aligns with global efforts to transition to cleaner energy sources and combat climate change.
RESS also enhances energy independence for homeowners. With the ability to store energy and manage its use, households become less dependent on the grid, providing a reliable power source even during outages or disruptions. This is particularly valuable in areas prone to natural disasters or where the grid infrastructure is less reliable.
Summary and Future Directions of Energy Storage Development
In summary, Residential Energy Storage Systems (RESS) represent a significant advancement in the way energy is managed and consumed in homes. By storing excess electricity generated from renewable sources like solar power, RESS allows homeowners to maximize their use of clean energy, reduce electricity costs, and increase energy independence. The core components, including high-quality batteries and efficient inverters, play a crucial role in ensuring the safety, reliability, and efficiency of these systems.
The future of energy storage, including RESS, is poised for continued growth and innovation. As battery technologies improve, we can expect to see advancements in energy density, cost reductions, and enhanced safety features. This will make energy storage systems more accessible and appealing to a broader range of consumers. Additionally, the integration of smart technologies and artificial intelligence will further optimize energy management, enabling more precise control over energy storage and usage.

Furthermore, the development of new storage technologies, such as solid-state batteries and flow batteries, holds promise for even greater efficiency and capacity. As the global energy landscape continues to evolve, with a growing emphasis on renewable energy and decarbonization, the role of energy storage systems will become increasingly vital. These systems will not only support the stability and reliability of the grid but also empower consumers to take control of their energy consumption and contribute to a more sustainable future.