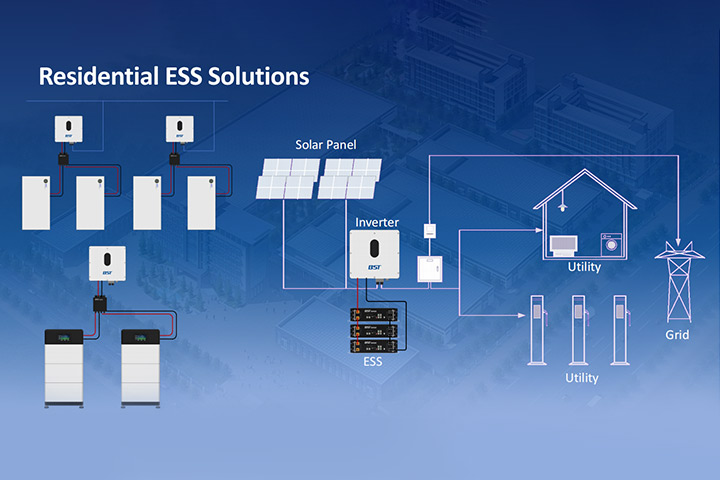
As the world shifts towards renewable energy solutions, residential energy storage systems have become essential in managing power consumption and storing surplus energy from solar panels. According to market reports, the global energy storage market is expected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 22% from 2023 to 2030, with household energy storage systems playing a significant role in this surge.
However, this rapid adoption brings a critical question: How can consumers ensure the safety, reliability, and performance of these systems? The answer lies in certifications. Certifications are not just technical standards—they are safeguards for consumers and the environment, ensuring that these energy storage batteries comply with international safety and quality benchmarks. Let’s explore the most important certifications for residential energy storage batteries.
Certifications: The Backbone of Safety and Quality
Certifications validate that energy storage batteries meet global safety, environmental, and quality standards. They ensure that these systems operate reliably, are safe to use, and can be transported and installed without risks. Below, we explore six essential certifications for household energy storage batteries and their significance.
1. CE-EMC: Electromagnetic Compatibility Certification
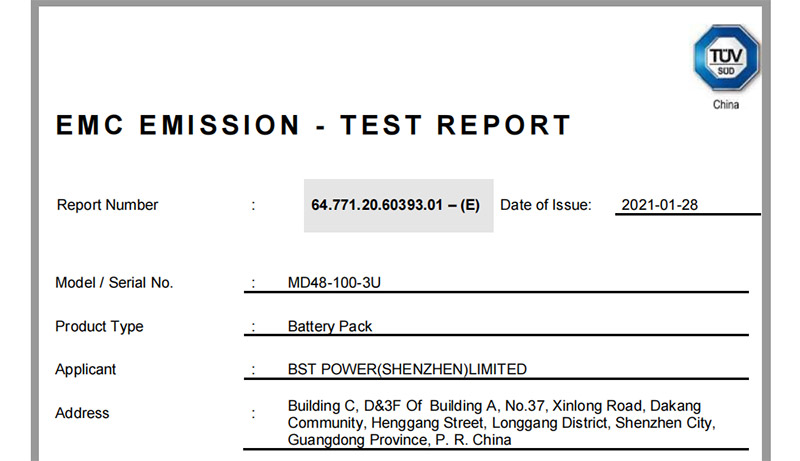
CE-EMC certification ensures that a product meets the European Union’s standards for electromagnetic compatibility. This is crucial for residential energy storage batteries because these devices often operate in environments with other electronic equipment.
Importance:
- Ensures that the battery does not emit electromagnetic interference (EMI) that could disrupt nearby electronic devices like Wi-Fi routers or medical equipment.
- Guarantees the battery’s immunity to external electromagnetic fields, enhancing operational reliability.
- Mandatory for products sold in the European Economic Area (EEA).
2. CE: Conformité Européenne Certification

CE mark is a general safety certification for products sold in the European Union. For energy storage batteries, CE certification ensures compliance with essential health, safety, and environmental standards.
Importance:
- Ensures the battery meets EU safety directives for electrical devices.
- Demonstrates that the product is free from hazardous components that may harm users or the environment.
- Signals that the manufacturer has adhered to strict quality control measures during production.
3. UL1973: Safety Standard for Batteries

UL1973 certification, issued by Underwriters Laboratories, evaluates the safety of stationary batteries used in residential energy storage systems. It is a benchmark for assessing the performance of batteries under normal and abnormal conditions.
Importance:
- Tests for potential risks such as thermal runaway, electrical faults, and mechanical damage.
- Verifies that batteries maintain integrity during high-temperature operations and overloads.
- Recognized globally, particularly in North America, as a key safety certification.
4. UN38.3: Lithium Battery Transportation Certification

UN38.3 certification is mandatory for transporting lithium batteries, including those used in energy storage systems. It ensures that batteries can safely endure the rigors of transportation.
Importance:
- Includes tests for altitude simulation, vibration, shock, thermal stability, and external short circuits.
- Reduces the risk of accidents during shipping, especially for international trade.
- A prerequisite for air, sea, and road transportation of lithium batteries.
5. IEC62619: Safety for Secondary Lithium Batteries
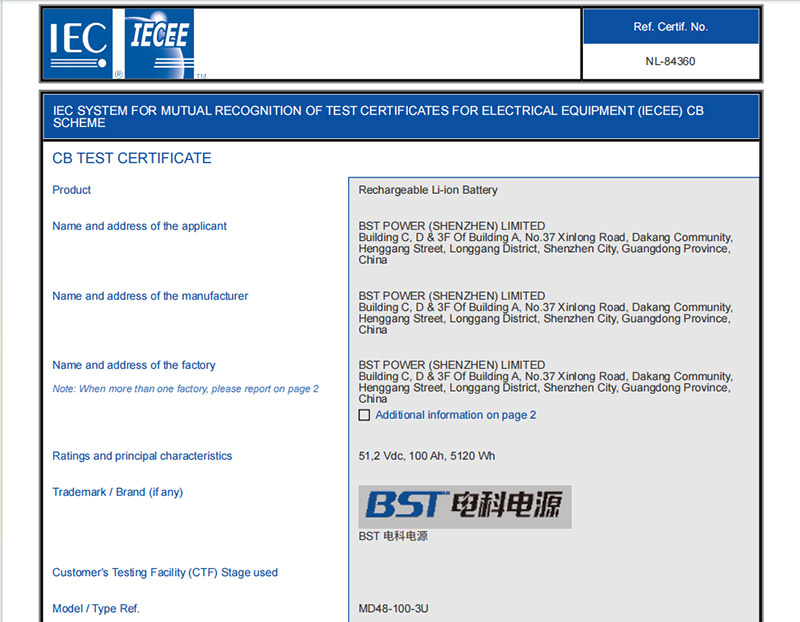
IEC62619 is an international safety standard specifically designed for secondary lithium batteries used in industrial and residential applications.
Importance:
- Focuses on the battery’s performance under thermal and electrical stress.
- Tests for overcharging, short circuits, and forced discharges, ensuring safe operation.
- Widely recognized in Europe, Asia, and other regions.
6. MSDS: Material Safety Data Sheet

An MSDS is not a certification per se but a document that provides comprehensive information about the materials used in the battery.
Importance:
- Details the chemical composition of the battery and associated hazards.
- Provides guidance on safe handling, storage, and disposal.
- Essential for ensuring workplace safety and environmental compliance.
Summary and Conclusion
Certifications are the backbone of the residential energy storage battery industry, ensuring safety, reliability, and environmental compliance. From the CE-EMC and UL1973 certifications that guarantee operational safety to UN38.3 which secures transportation, each certification plays a vital role in bringing trustworthy products to market.
As the demand for residential energy storage grows, manufacturers must prioritize these certifications to gain consumer trust and access global markets. For consumers, understanding these certifications empowers them to make informed decisions, ensuring they invest in systems that are safe, durable, and environmentally friendly.
Answers to 6 RFQs on Residential Energy Storage Certifications
1. Why is CE-EMC certification mandatory for European residential energy storage batteries?
CE-EMC certification ensures electromagnetic compatibility, meaning the battery won’t emit interference that could disrupt other devices, such as medical equipment or communication systems. This certification also ensures that the battery is immune to external electromagnetic disturbances, reducing the risk of malfunction in environments with high EMI levels.
2. How does the UL1973 certification enhance fire safety for residential energy storage systems?
UL1973 evaluates a battery’s ability to withstand thermal runaway, overcharging, and physical damage. By simulating real-world scenarios like electrical faults and high temperatures, this certification ensures that the battery won’t catch fire or explode during normal operation or under fault conditions, significantly enhancing fire safety.
3. What are the risks of purchasing energy storage batteries without UN38.3 certification?
Without UN38.3 certification, there’s a higher risk of accidents during transportation due to untested batteries. These risks include explosions, fires, or leaks caused by altitude pressure changes, vibrations, or shocks during transit. Moreover, many carriers and customs offices will refuse to handle uncertified batteries, complicating logistics.
4. How can IEC62619-certified batteries improve performance and safety compared to uncertified alternatives?
IEC62619 certification ensures that batteries are tested for overcharging, short circuits, and other stress scenarios. Certified batteries perform reliably under extreme conditions, providing consistent energy output and reducing the likelihood of failures that could compromise household safety or disrupt energy storage.
5. Why is MSDS documentation critical for end-users and regulatory compliance?
The MSDS provides detailed information on the battery’s chemical composition, hazards, and handling instructions. This transparency ensures that users and installers handle the battery safely and can respond effectively to emergencies, such as leaks or fires. It also helps meet regulatory requirements for workplace and environmental safety.
6. Are there additional certifications required for residential energy storage batteries in specific countries?
Yes, certain countries have unique requirements. For example, in the U.S., batteries may require FCC compliance for electromagnetic interference, while Australia often mandates Clean Energy Council (CEC) certification. In China, GB standards (national standards) regulate battery safety and performance. Manufacturers should always check regional certification requirements to ensure compliance.