I. Introduction
Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are one of the most widely used rechargeable battery technologies in the world today. They power everything from smartphones and laptops to electric vehicles (EVs) and home energy storage systems. Known for their high energy density, lightweight design, and long lifespan, Li-ion batteries have revolutionized portable power solutions.

With the increasing demand for sustainable energy storage and the rapid growth of electric mobility, the global lithium-ion battery market is expanding rapidly. Industry analysts predict that the market will continue to grow as advancements in battery technology improve efficiency, safety, and environmental sustainability.
II. Structure and Working Principle of Lithium-Ion Batteries
1. Key Components
A lithium-ion battery consists of several crucial components:
- Cathode: The positive electrode, typically made from lithium-based materials such as lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO₂), lithium iron phosphate (LiFePO₄), or lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (NMC).
- Anode: The negative electrode, commonly composed of graphite.
- Electrolyte: A liquid or solid substance that facilitates lithium-ion movement between the cathode and anode during charging and discharging.
- Separator: A thin layer that prevents direct contact between the cathode and anode while allowing ion transfer.
2. How Lithium-Ion Batteries Charge and Discharge
The working principle of a lithium-ion battery is based on the movement of lithium ions between the electrodes:
- Charging Process: When the battery charges, lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode through the electrolyte, storing energy.
- Discharging Process: When the battery is in use, lithium ions flow back from the anode to the cathode, generating electricity.
This reversible process allows lithium-ion batteries to be recharged multiple times while maintaining high efficiency.
3. Advantages of Lithium-Ion Battery Technology
- High Energy Density: Li-ion batteries store more energy per unit weight than traditional lead-acid or nickel-based batteries.
- Low Self-Discharge Rate: Unlike older battery types, lithium-ion batteries lose very little charge when not in use.
- No Memory Effect: Users can recharge them at any time without reducing their lifespan.
III. Types of Lithium-Ion Batteries
Different lithium-ion battery chemistries offer unique characteristics suited to various applications:
1. NMC (Nickel Manganese Cobalt) Batteries
- Widely used in electric vehicles and energy storage systems.
- Offers a balance between energy density, lifespan, and cost.
2. LFP (Lithium Iron Phosphate) Batteries
- Known for excellent thermal stability and safety.
- Commonly used in home energy storage and commercial applications.
3. NCA (Nickel Cobalt Aluminum) Batteries
- Provides high energy density, primarily used in high-performance electric vehicles.
- Used by major EV manufacturers like Tesla.
4. Comparison of Different Lithium-Ion Chemistries
| Battery Type | Energy Density | Safety | Cycle Life | Cost |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NMC | High | Moderate | Moderate | Medium |
| LFP | Moderate | High | Long | Lower |
| NCA | Very High | Low | Moderate | Higher |
IV. Applications of Lithium-Ion Batteries
1. Consumer Electronics
Li-ion batteries are essential for powering smartphones, laptops, tablets, and smartwatches due to their compact size and high energy efficiency.
2. Electric Vehicles (EVs)
EV manufacturers prefer lithium-ion batteries because they offer long driving ranges, fast charging times, and lightweight properties.
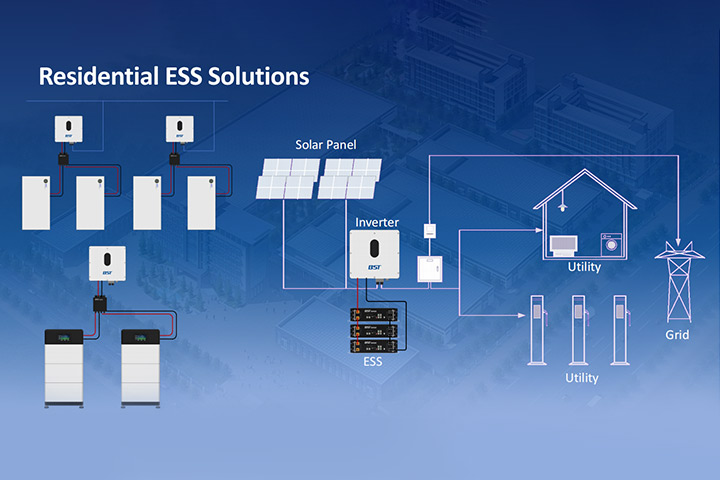
3. Home and Industrial Energy Storage Systems
Used in residential solar energy storage solutions and large-scale industrial backup power systems to ensure reliable electricity supply.
4. Power Tools and Medical Devices
Many cordless power tools and life-saving medical devices, such as pacemakers, use lithium-ion technology for its reliability and long cycle life.
V. Advantages and Disadvantages of Lithium-Ion Batteries
1. Advantages
- Lightweight and Compact: Compared to lead-acid batteries, they offer the same power at a fraction of the weight.
- Long Cycle Life: Can last for thousands of charge-discharge cycles, reducing long-term replacement costs.
- High Efficiency: Lithium-ion batteries have an energy conversion efficiency of over 90%.
2. Disadvantages
- Thermal Runaway Risk: Overcharging or physical damage can lead to overheating and fire hazards.
- Cost: Higher initial investment compared to traditional battery technologies.
- Recycling Challenges: The disposal of lithium-ion batteries requires specialized processes to recover valuable materials and prevent environmental pollution.
VI. Market Overview and Future Development
1. Current Global Lithium-Ion Battery Market Status
The demand for lithium-ion batteries is surging due to the rise of electric vehicles, renewable energy storage, and technological advancements. Governments worldwide are investing in battery technology to reduce carbon emissions and transition to clean energy solutions.
2. Growth Potential in Renewable Energy and EV Sectors
- By 2030, global battery production is expected to exceed 5 TWh per year.
- The EV market is projected to drive over 70% of lithium-ion battery demand.
3. Technological Innovations and Next-Generation Batteries
- Solid-State Batteries: Offer higher safety and energy density, currently in research and development.
- Recycling and Second-Life Batteries: Companies are focusing on battery reuse to improve sustainability.
VII. BST’s History and Expertise in 26650 Lithium-Ion Batteries
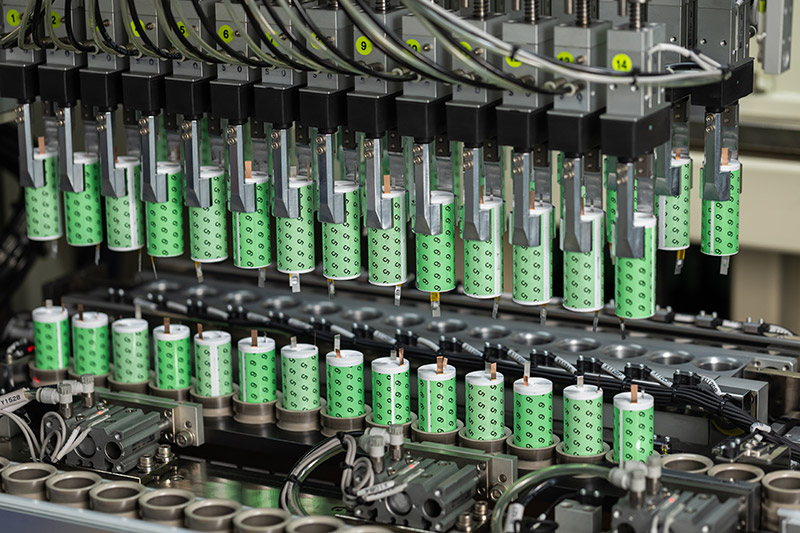

BST has been a leading manufacturer in the battery industry for 22 years, specializing in 26650 lithium-ion batteries. Over the years, BST has built a strong reputation for high-performance battery solutions, trusted by global clients.
1. Specialization in 26650 Battery Production
BST’s 26650 batteries are known for their:
- High energy density for long-lasting power.
- Excellent safety performance with advanced thermal management.
- Long cycle life for sustainable applications.
2. R&D Capabilities and Quality Control
BST invests heavily in research and development to enhance battery performance. Every battery undergoes strict quality control to meet international safety standards.
3. Global Market Presence and Customer Trust
With customers across Europe, North America, and Asia, BST has established itself as a preferred supplier of high-quality lithium-ion batteries for EVs, energy storage, and industrial applications.
4. Vision for a Green Energy Future
BST is committed to sustainable battery technology, contributing to a low-carbon future with innovative and eco-friendly energy storage solutions.
VIII. Conclusion
Lithium-ion batteries have become the backbone of modern energy storage, powering everything from electronics to electric vehicles. With continuous innovation and increasing demand, their role in a clean energy future is undeniable.
For businesses looking for reliable 26650 battery solutions, BST stands out as a leader in quality, expertise, and sustainability. By choosing BST’s 26650 lithium-ion batteries, customers gain access to high-performance, long-lasting, and eco-friendly energy solutions for diverse applications.
In conclusion, the 26650 lithium-ion battery’s powerful performance, long cycle life, and safety make it ideal for a wide range of applications. These include E-Mobility scooters, AGVs (automated guided vehicles), security alarms, gardening tools, forklifts, baby strollers, 36V golf carts, electric wheelchairs, medical device batteries, ventilator batteries, RVs (12.8V), yachts, pickups, tricycles, UPS batteries for telecom base stations, solar streetlights, solar trackers, emergency lights (Ni-CD, Ni-MH), and various industrial applications.
As a trusted leader in 26650 battery production, BST continues to deliver high-quality, innovative energy solutions tailored to meet the evolving demands of these diverse sectors.